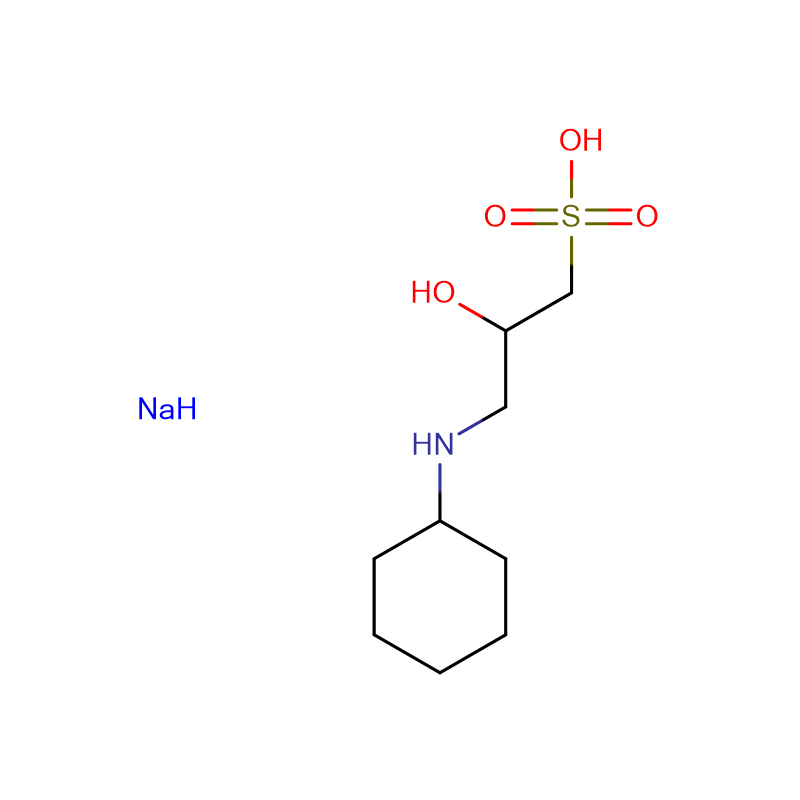
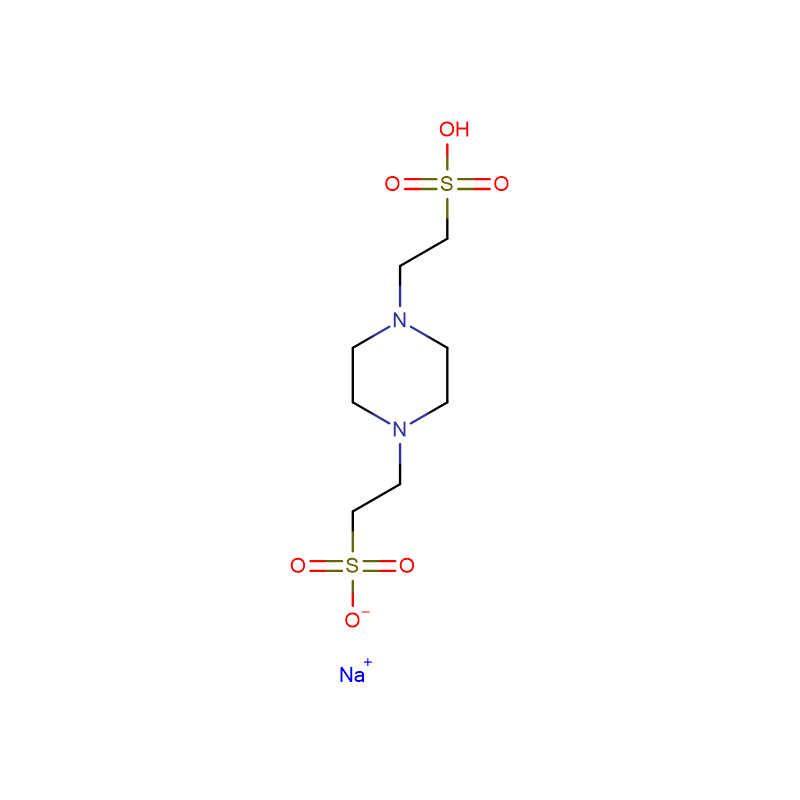
MOBS Cas:115724-21-5 4 -Morpholinobutane -1-sulfonic acid 99% Pale yellow solid
| Catalog Number | XD90096 |
| Product Name | MOBS |
| CAS | 115724-21-5 |
| Molecular Formula | C8H17NO4S |
| Molecular Weight | 223.29 |
| Storage Details | Ambient |
| Harmonized Tariff Code | 2921300090 |
Product Specification
| Appearance | Pale yellow solid |
| Assay | ≥99% |
| Storage Temp | Store at RT |
| Density | 1.2045 (rough estimate) |
| Melting point | >300 ºC |
| Refractive index | 1.5364 (estimate) |
| PH | 3.0-5.0 (25℃, 0.5M in H2O) |
| Solubility | H2O: 0.5 M at 20 °C, clear, colorless |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| Acidity coefficient (pKa) | 9.3(at 25℃) |
A biological buffer is an organic substance that has a neutralizing effect on hydrogen ions. In this way, a biological buffer helps maintain the body at the correct pH so that biochemical processes continue to run optimally.
Most buffers consist of a weak acid and a weak base. They help maintain a given pH even after the addition of an acid or a base. For example, blood contains a carbonic acid (H2CO3)-bicarbonate (HCO3-) buffer system. In this system, the weak acid dissociates to a small extent, giving bicarbonate ions. These ions are capable of binding extra H+ions floating around in the blood. This reforms the weak acid and reduces the amount of H+ ions in solution.
Biological buffers can also be buffer systems that help maintain a steady pH around the physiological pH. When conducting experiments with individual components of cells or individual proteins, scientists must take into account the buffer they use. Without a good buffer, the activity of the component they want to study may decrease.
Buffers are chemicals that help a liquid resist changing its acidic properties when other chemicals are added that will normally cause a change in these properties. Buffers are essential for living cells. This is because buffers maintain the right pH of a liquid.What is pH? It's a measure of how acidic a liquid is. For example, lemon juice has a low pH of 2 to 3 and is very acidic -- so is the juice in your stomach that breaks down food. Since acidic liquids can destroy proteins, and cells are chock-full of proteins, cells need to have buffers inside and outside them in order to protect their protein machines. The pH inside a cell is about 7, which is considered neutral like pure water.



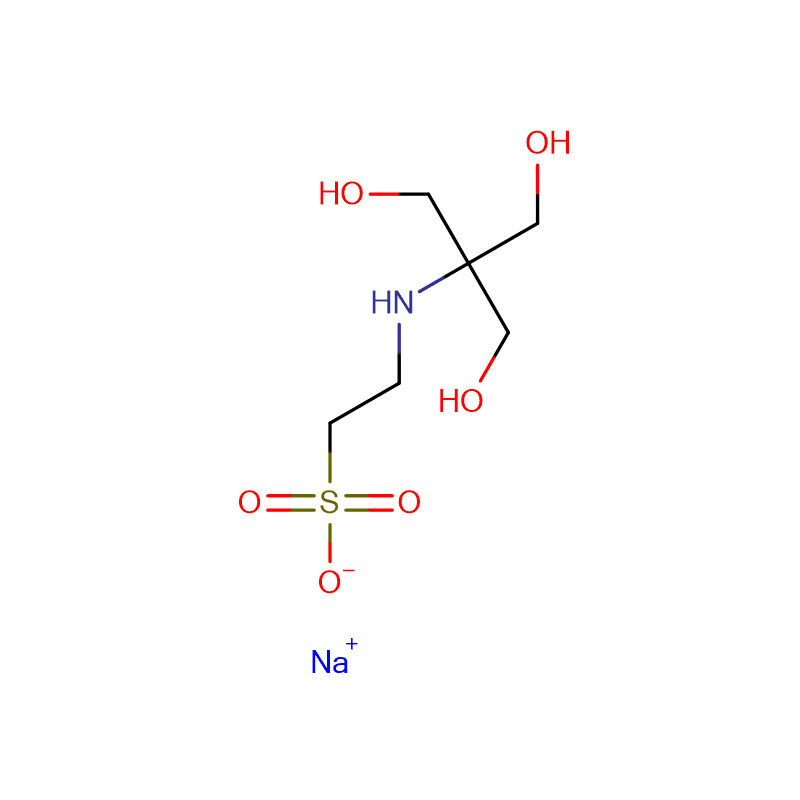

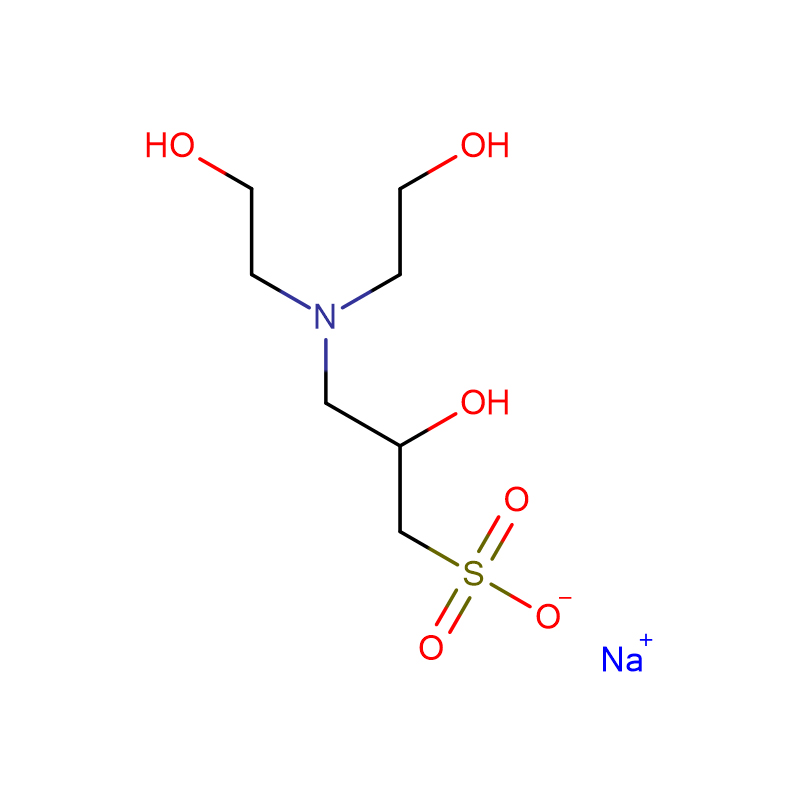
![disodium 4-[3-methyl-N-(4-sulfonatobutyl)anilino]butane-1-sulfonate Cas:127544-88-1](https://cdn.globalso.com/xdbiochems/127544-88-1.jpg)