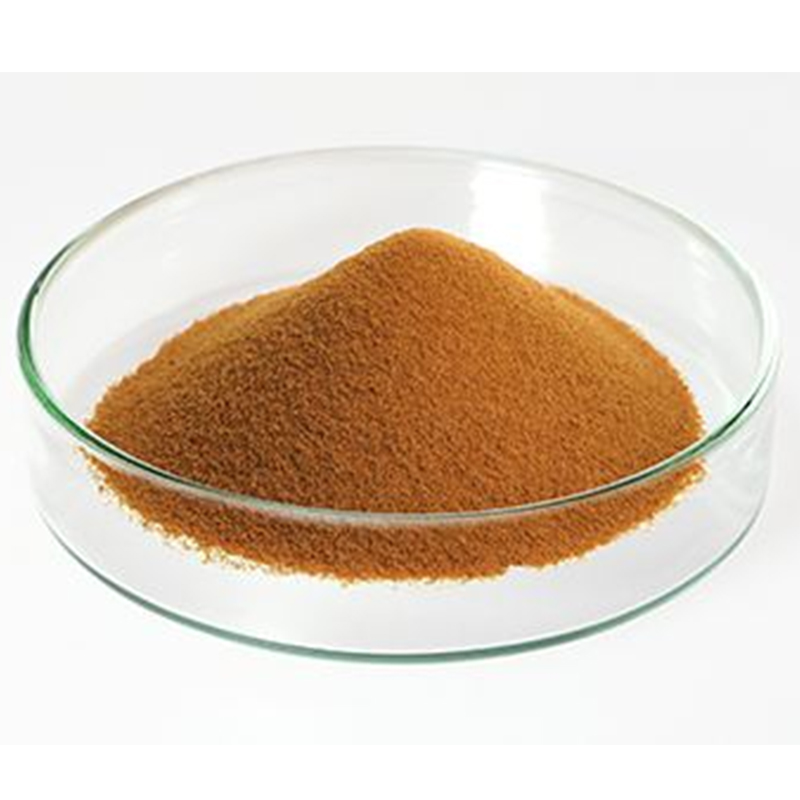
Cytochrome C CAS:9007-43-6 Reddish or dark brown powder
| Catalog Number | XD90330 |
| Product Name | Cytochrome C |
| CAS | 9007-43-6 |
| Molecular Formula | C42H54FeN8O6S2 |
| Molecular Weight | 886.91 |
| Storage Details | -15 to -20 °C |
| Harmonized Tariff Code | 35040090 |
Product Specification
| Appearance | Reddish or dark brown powder |
| Assay | 99% |
| pH | 5 - 7 |
| Iron | 0.40 - 0.48% |
| Purity | Min 90% |
| Residue on Ignition | Max 1.5% |
| Moisture | Max 6% |
| Sterility | Complies with sterility test |
| Pyrogens | Free |
| Colorimetric Test | Positive |
| E. Coli | Absent |
| Salmonella Species | Absent |
| Solubility 10% in water | Clear with red color |
| Extinction value | Er/Eo:Min1.1 |
| Total Microbial Count cfu / g | Max 100 |
| Moulds/Yeasts | Absent |
| Origin | Horse heart |
An emerging literature suggests that bisphenol A (BPA), a widespread endocrine disrupting chemical, when exposure occurs in early life, may increase the risk of metabolic syndrome. In this study, we investigated the hypothesis that perinatal exposure to BPA predisposed offspring to fatty liver disease: the hepatic manifestation of metabolic syndrome, and its possible mechanism. Pregnant Wistar rats were administered with BPA (40μg/kg/day) or vehicle during gestation and lactation. Liver histology, biochemical analysis, transcriptome, and mitochondrial function were examined in male offspring at postnatal 3, 15 and 26 weeks. At 3 weeks of age, abnormal liver morphology and function were not observed in the BPA-exposed offspring, but a decrease in mitochondrial respiratory complex (MRC) activity (I and III) and significant changes in gene expression involved in mitochondrial fatty acid metabolism were observed compared with controls. At 15 weeks, micro-vesicular steatosis in liver, up-re gulated genes involved in lipogenesis pathways, increased ROS generation and Cytc release were observed in the BPA-exposed offspring. Then, extensive fatty accumulation in liver and elevated serum ALT were observed in BPA-exposed offspring at 26 weeks. In the longitudinal observation, hepatic mitochondrial function including MRC activity, ATP production, ROS generation and mitochondrial membrane potential were progressively worsened in the BPA-exposed offspring. Perinatal BPA exposure contributes to the development of hepatic steatosis in the offspring of rats, which may be mediated through impaired hepatic mitochondrial function and up-regulated hepatic lipid metabolism.